Your blood vessels are continually working as long as you are still alive. This constant motion of blood and other substances may result in blockages or wear-and-tear of blood vessel walls or other features. These issues may be hard to notice, and only thorough tests and procedures may be done to solve them. An example of such a procedure is Evergreen Park carotid stenting. More about carotid stenting and all it involves is discussed below.
What is carotid stenting?
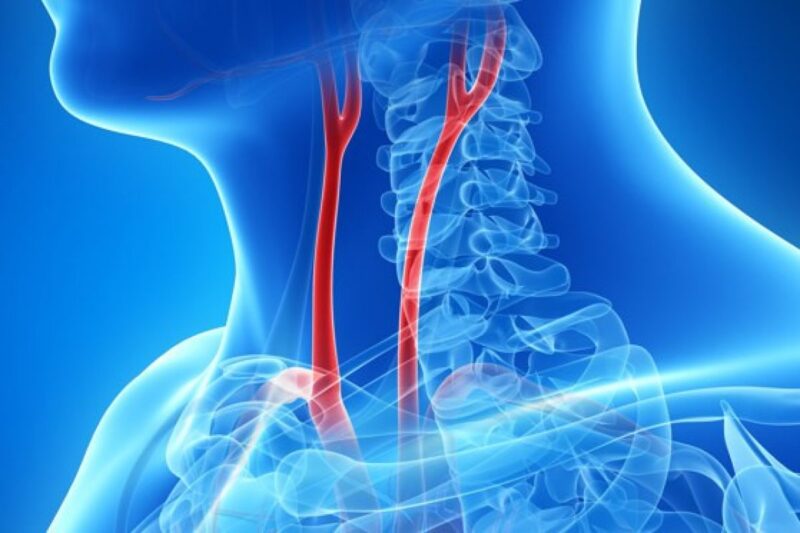
Carotid stenting is an operation done to unblock clogged arteries, thereby returning blood flow to the brain. This is done mainly to prevent or treat strokes.
The carotid arteries are the primary suppliers of blood to the brain and are found on either side of the neck. Fatty deposits may accumulate in these vessels, thus clogging or slowing down the flow of blood to your brain, resulting in a stroke. This condition is referred to as carotid artery disease.
Before carotid stenting is done, another procedure known as carotid angioplasty is done. These two procedures are done together to achieve the best results.
A small balloon is usually inflated and temporarily introduced into the blocked blood vessel, thus increasing its width, enabling undisturbed blood flow to the brain. A tiny coil of metal is typically placed in the affected artery. This keeps the artery open while reducing the likelihood of becoming narrow again.
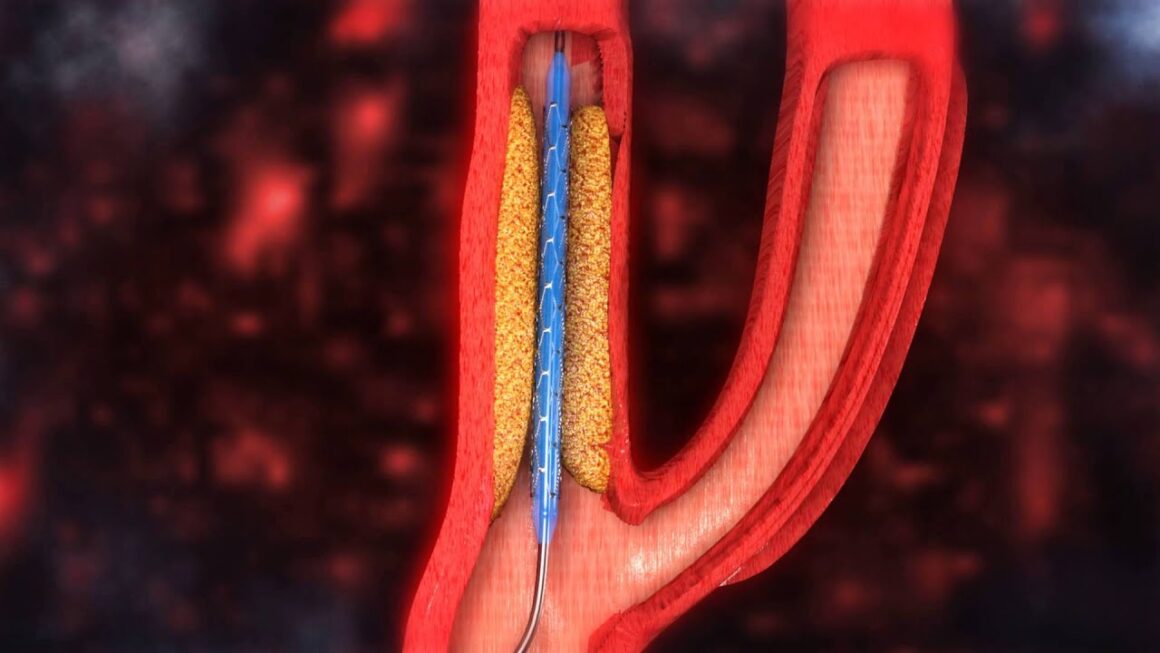
These procedures are usually done if standard carotid surgery is deemed too risky or impossible. They are suitable to prevent or treat strokes if:
- You have already gotten a carotid endarterectomy, and narrowing begins to occur again after the surgery
- Most of your artery is clogged, and stroke or its symptoms begin to appear. You may also be too weak for surgery, especially if you have gone through severe lung or heart disease.
- The narrowing has happened in a position that is challenging to access.
Your physician will discuss the best possible options with you before a decision is made.
Some typical complications arising from the procedure include:
- New narrowing of the vessels after surgery despite the additional stents
- Blood clots and dislodging of plaque when threading the catheter may cause a stroke mid-operation
- Bleeding at the area in which the catheters were introduced
Results
This procedure typically aims to elevate the flow of blood in the affected artery, reducing the chances of a stroke occurring.
Medical intervention is required if the symptoms before the procedure come back. Newer symptoms like numbness on one body side or trouble speaking or walking may also happen. If they do, be sure to call your doctor.
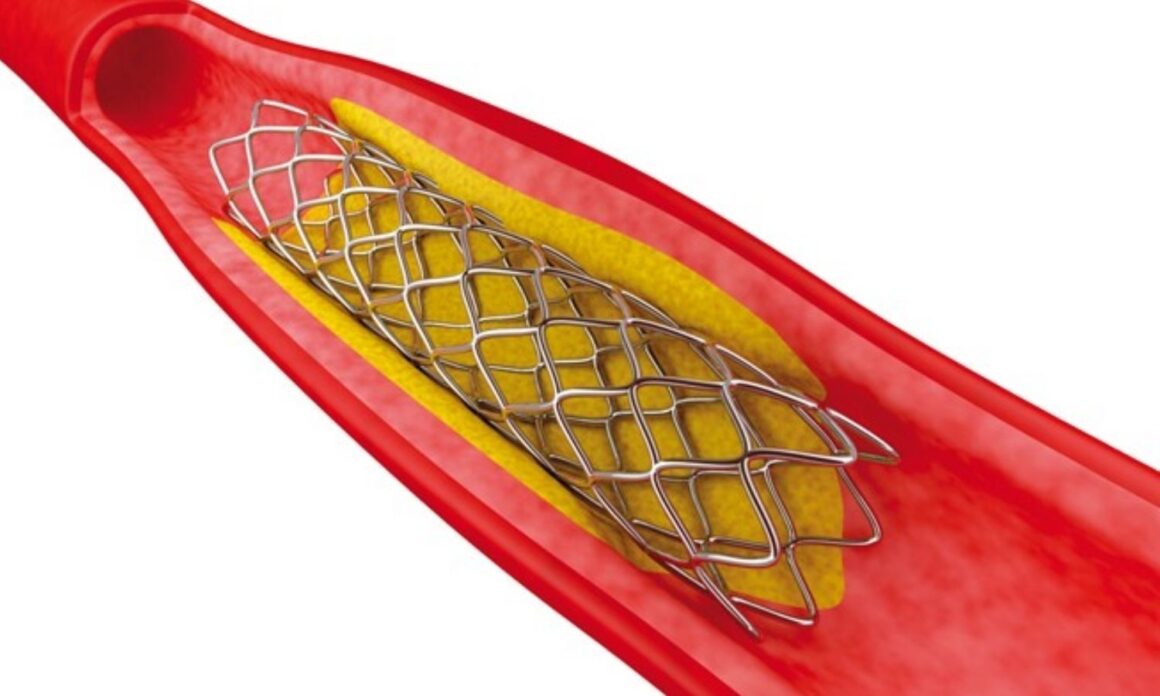
Lifestyle changes that may enable you to keep up the good results include:
- Reducing your levels of triglyceride and cholesterol
- Not smoking
- Controlling other conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
Carotid stenting is a nonsurgical operation that offers minimal invasion compared to surgery. Thus it may be performed when awake, and the recovery time after the procedure is usually minimal. For any carotid stenting questions, visit us online, or call our offices in Tinley Park, IL.